Australia's electric vehicle (EV) market is rapidly expanding, with Tesla leading the high-end segment and Chinese brands like BYD and Anari gaining traction among mid-to-low-end consumers. In the first half of 2023, EV sales more than doubled, capturing 7.2% of the market, driven by rising environmental awareness and economic factors, particularly in urban and coastal areas. However, the market's growth is constrained by limited charging infrastructure, despite recent investments in public charging networks.
Government policies at federal, state, and local levels are pivotal, with varying degrees of support through subsidies, tax incentives, and infrastructure development. The market is expected to diversify further with more brands entering and an accelerated rollout of charging stations, enhancing the viability of EVs across Australia.
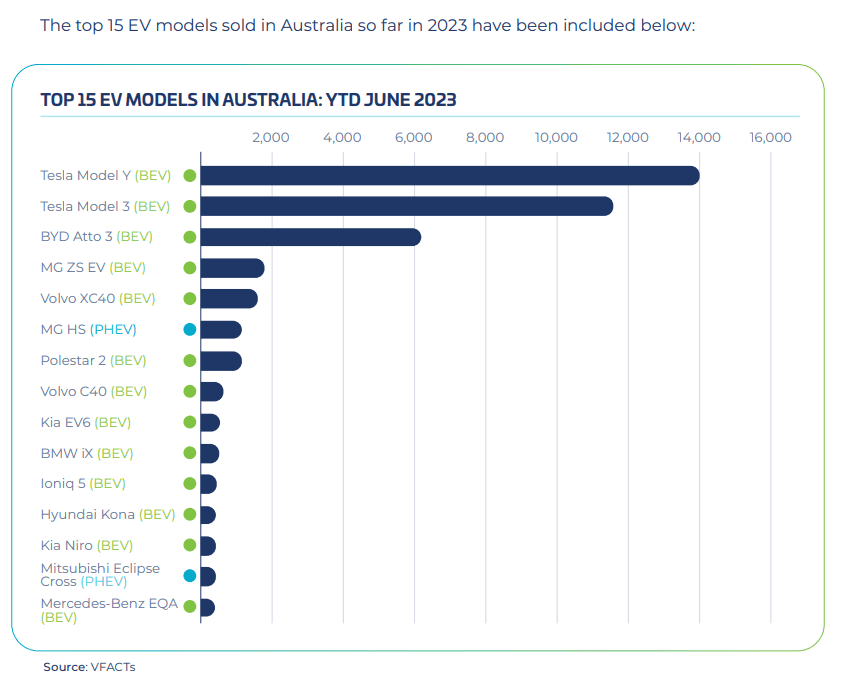
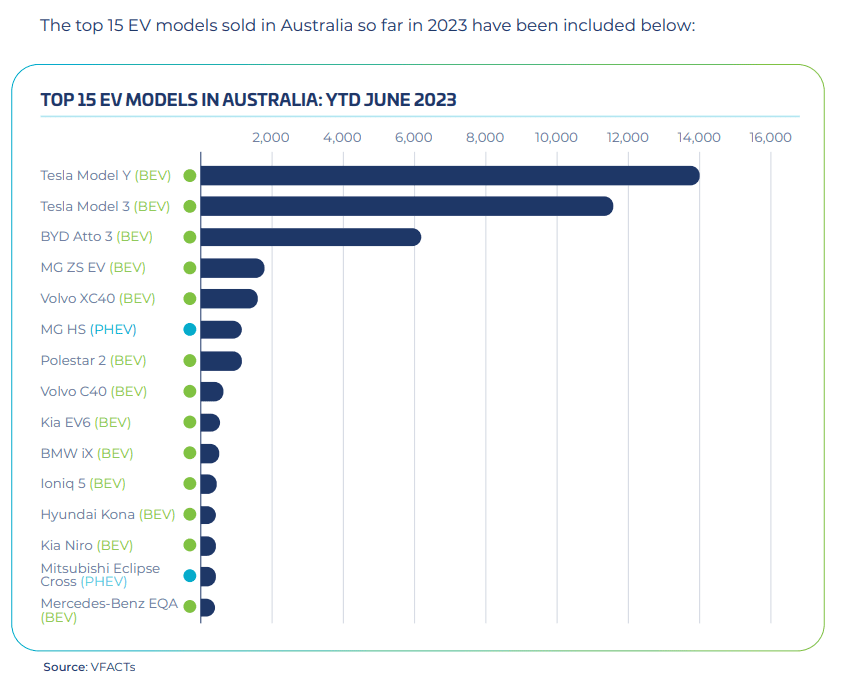
The electric vehicle market in Australia is dominated by Tesla and Chinese brands. The former occupies the high-end market share with its high-end, high-performance, and high-intelligence product image, while the latter attracts mid-to-low-end consumers with its advantages of lower price, efficiency, and safety. According to VFACTS data, in the first half of 2023, among the top 15 electric vehicle models in Australia, Tesla ranked first, among which Chinese brands include BYD, Polestar, and MG.
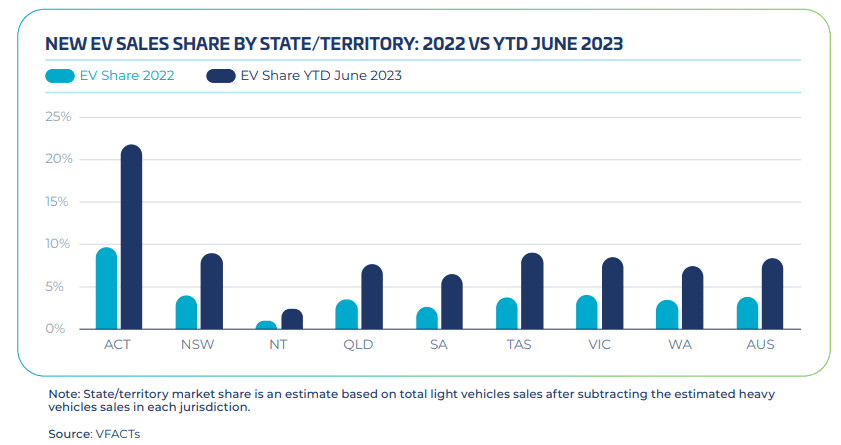
The consumer group of Australia's electric vehicle market is mainly concentrated in urban and coastal areas, where the population density and the economic level is higher, the environmental awareness is stronger, and the demand and acceptance of electric vehicles are higher. According to the data of the Federal Automobile Industry Association (FCAI) of Australia, the sales of electric vehicles in Australia will more than double to 87,217 in 2023. This is equivalent to a market share of 7.2%, far higher than the 3.1% in 2022. In contrast, the sales of electric vehicles in regions such as China, the European Union, and the US account for more than 10%. The main groups of electric vehicle sales in Australia come from New South Wales, Victoria, and Queensland, all of which are the population and economic centers of Australia, as well as coastal states. The consumer group of Australia's electric vehicle market is mainly individuals and families. These consumers usually have a certain understanding and interest in electric vehicles, believing that electric vehicles are a more environmentally friendly, economical, and advanced way of transportation, and are willing to pay a certain premium for it. According to data from the Electric Vehicle Council, in the first half of 2023, 80% of electric vehicle sales in Australia were purchased by individuals or families, rather than by businesses or governments.
The share of EV in each region is as follows:
The consumer group of Australia's electric vehicles market mainly focuses on factors such as price, range, charging, and performance of electric vehicles, which directly affect their willingness and satisfaction with electric vehicle purchases. According to data from the Electric Vehicle Council, in the first half of 2023, 60% of potential buyers of electric vehicles in Australia said they were most concerned about the price of electric vehicles, 50% said they were most concerned about the range of electric vehicles, 40% said they were most concerned about the charging, and 30% said they were most concerned about the performance of electric vehicles.
The best-selling EV brands in Australia are as follows:
According to the Electric Vehicle Council's (EVC) 2023 report :
Number of public charging stations : In 2023, there are approximately 4,943 public charging stations in Australia, including 558 high-power charging stations. The number of these high-power charging stations has increased by 57% compared to 2022.
Fast charging stations : The 558 high-power public charging stations mentioned above can provide fast charging services, and most stations are equipped with multiple charging sites, which can charge multiple electric vehicles at the same time.
Statewide charging network : In South Australia in particular, the government has partnered with private investors to build Australia's first statewide electric vehicle charging network, further boosting charging infrastructure coverage in the region.
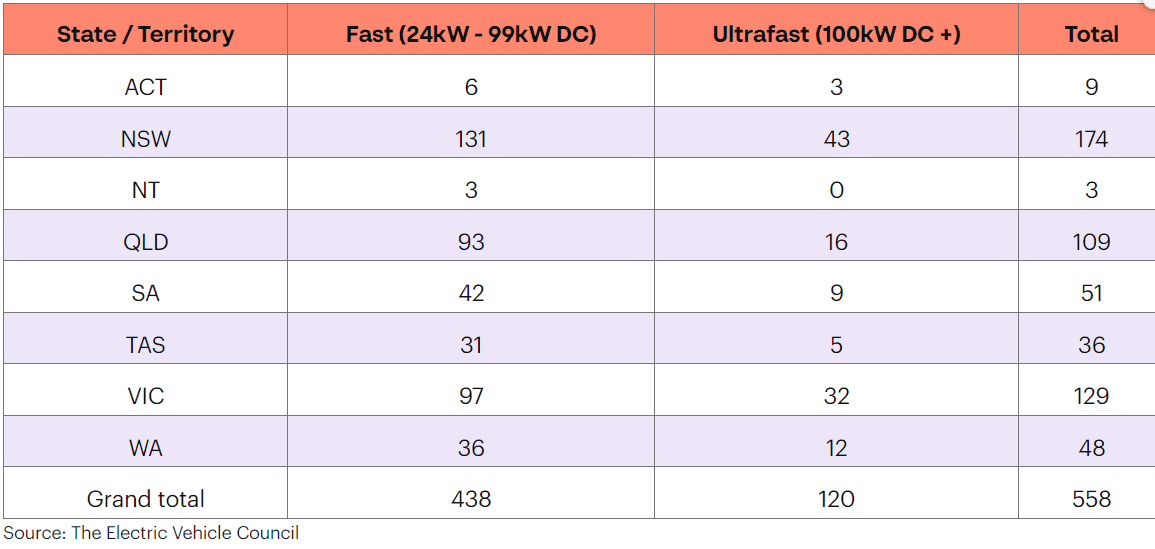
The following chart is from the EVC report, outlining the number of fast and ultra-fast charging points in each state and region. NSW has the highest number of high-power charging stations, with 174.
Plugshare
Source:https://www.plenti.com.au/guides/public-ev-charging-australia/
The development of the electric vehicle and charging market in Australia has been influenced by the government. Different policies and measures have different stimulating and inhibitory effects on the market. Currently, some states have even imposed additional road use taxes on electric vehicles, which has hindered the promotion of electric vehicles. However, some state and local governments have taken some positive measures, such as providing car purchase subsidies, exempting vehicle taxes, free parking, and using bus lanes, to encourage the use of electric vehicles. In addition, the Australian government is also increasing investment in EV charging infrastructure, supporting the construction of more charging stations nationwide through projects such as the Future Fuel Fund to meet the charging needs of electric vehicle users.
The electric vehicle and charging industry in Australia is a complex industry involving multiple fields and links, which can be subdivided from the following aspects:
Subdivision of electric vehicles:
According to the different power systems, electric vehicles can be divided into battery electric vehicles (BEV), plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEV), and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV). According to the different models, electric vehicles can be divided into sedans, SUVs, pickups, commercial vehicles, etc. According to the different prices, electric vehicles can be divided into high-end, mid-range, and low-end.
Charging station segmentation:
According to the different charging methods, charging stations can be divided into wired charging and wireless chargin. According to the different charging speeds, charging station can be divided into slow charging, fast charging and ultra-fast charging. According to the different charging scenarios, it can be divided into public charging and private charging. According to the different charging standards, it can be divided into CCS, CHAdeMO, GB/T and Tesla, etc.
Electric vehicles and charging industry chain segmentation:
The electric vehicle and charging industry chain includes upstream raw material supply, midstream component manufacturing and vehicle assembly, downstream sales and services. Among them, upstream raw material supply mainly involves rare metals and chemicals such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, as well as the production of core components such as batteries, motors, and electronic controls; midstream component manufacturing and vehicle assembly mainly involve the processing and assembly of automotive components, as well as the design and manufacturing of electric vehicles; downstream sales and services mainly involve the distribution and retail of electric vehicles, as well as the construction and operation of charging stations.
Government policy on electric vehicles and charging stations in Australia
The development of electric vehicles and charging stations in Australia has been influenced by the government. Different levels of government have different stimulating and inhibitory effects on the market. Currently, the policy environment in Australia can be analyzed from the following aspects.
Federal government policy:
The federal government is the highest level of government in Australia, and its policies have important guidance and influence on the national market.
On April 19, 2023, the federal government of Australia officially released the National Electric Vehicle Strategy. This strategy marks an important step for Australia in promoting the popularization of electric vehicles and addressing climate change.
The core objectives of the strategy include:
Increase the supply of electric vehicles : Ensure consumers have more choices by promoting more affordable and easily accessible electric vehicles into the market.
Build the necessary infrastructure : To accelerate the popularization of electric vehicles, the government plans to establish a nationwide charging network and simplify the charging process of electric vehicles. The strategy also emphasizes the construction of resources and systems to support the rapid development of electric vehicles.
Encouraging demand for electric vehicles : The government will take a number of measures to incentivize consumers to switch to electric vehicles, including possible tax incentives and other forms of economic incentives.
The release of this strategy reflects the Australian government's commitment to sustainable transportation and lays the policy foundation for the rapid development of the electric vehicle industry. Through this strategy, Australia hopes to accelerate the popularization of electric vehicles, reduce carbon emissions in the transportation sector, and help the country achieve net zero emissions.
The state government is the second highest level of government in Australia, and its policies have a direct impact and regulatory role on the markets of each state. Different state governments have different attitudes and levels of support for electric vehicles and charging stations. The following is an overview of electric vehicle policies in some major states and territories.
1. UNSW State of Wales (NSW)
Tax incentives : Stamp duty exemption for electric vehicles priced below $78,000.
Subsidies : Subsidies of up to AUD $3,000 are available to individuals who purchase an electric vehicle (for vehicles within a certain price range).
Infrastructure investment : Plans to build more charging stations statewide and provide funding to support related projects.
2. Victoria (VIC)
Electric Vehicle Subsidy : A subsidy of up to $3,000 is offered to consumers who purchase a new electric vehicle.
Infrastructure building : Millions of dollars invested to expand the electric vehicle charging network and install more charging stations on major transport routes and urban areas.
Road use tax : Introduce a road use tax for electric vehicles, charged per kilometer traveled.
3. Queensland (QLD)
Electric Vehicle Subsidy : Provides up to $3,000 in subsidies to encourage consumers to buy electric vehicles.
Infrastructure development : The Queensland government has launched the "Electric Superhighway" program to build a statewide electric vehicle charging network.
4. South Australia (SA)
Statewide charging network : The government has established a statewide electric vehicle charging network by partnering with private investors.
Incentives : Provide stamp duty exemption for electric vehicles and a three-year fee waiver for electric vehicle registration.
5. Western Australia (WA)
Infrastructure investment : Millions of dollars will be invested in building Western Australia's charging network, including fast charging stations along long-distance roads.
Electric Vehicle Promotion : Introduce multiple policy incentives to encourage individuals and businesses to purchase electric vehicles.
6. Tasmania (TAS)
Tax incentives : Stamp duty exemption for individuals purchasing electric vehicles.
Infrastructure expansion : Invest in expanding electric vehicle charging facilities in the state, especially in tourist hotspots.
7. Australia Capital Territory (ACT)
Electric vehicle concession : Stamp duty exemption and two-year reduction in vehicle registration fees are provided.
Zero emissions target : The ACT Government plans to make all new car sales zero emission vehicles by 2030.
8. Northern Territory (NT)
Electric Vehicle Incentives : Provide stamp duty relief and vehicle registration fee relief.
Infrastructure planning : Electric vehicle charging networks are being planned and built to cover a wider area.
The electric vehicle policies of each state and territory reflect the enthusiasm of local governments in promoting clean energy transportation. These measures are not only aimed at encouraging the purchase of electric vehicles, but also at building a sound charging infrastructure to support the popularization of electric vehicles throughout Australia. For example, the NSW government launched an electric vehicle strategy worth 491 million AUD in June 2021. The strategy includes providing a subsidy of 3000 AUD for the first 25,000 consumers who purchase electric vehicles worth less than AUD 68,000, exempting stamp duty for electric vehicles, providing free national park passes for electric vehicles, providing priority parking spaces and bus lanes for electric vehicles, and building over 78,000 charging points statewide. The goal of the strategy is to have electric vehicles account for half of new car sales by 2030 and half of all vehicles by 2035. On the contrary, the Victorian government began imposing a 2.5 Australian cents/kilometer road use tax on electric vehicles in May 2021, which is considered a penalty for electric vehicles and will hinder the popularization and development of electric vehicles.
In addition, the South Australia Government has secured private investment to build an electric vehicle charging network in South Australia, and provided the Royal Automobile Association of Australia (RAA) with a grant of $12.35 million to build and operate Australia's first statewide electric vehicle charging network.
See: www.energymining.sa.gov.au
Source:Electric vehicles
Local government policies:
Local governments are the lowest level of government in Australia, and their policies have specific implementation and service roles for the markets in various regions. Some local governments have strong support for electric vehicles and charging stations, and provide convenience and discounts through cooperation with enterprises, communities, schools, etc., such as free or low-priced charging services, parking discounts, environmental education, etc., to promote the use and promotion of electric vehicles. For example, the Brisbane City Council launched a plan called "eBrisbane" in July 2021, which includes providing more electric vehicles for the city government's fleet, providing free electric vehicle sharing services for citizens, providing more charging stations for the city, and providing information and education on electric vehicles for citizens. The plan aims to make Brisbane one of the most electric vehicle-friendly cities in Australia by 2031.
In Australia, in addition to the electric vehicle (EV) policies formulated by the federal and state governments, local governments (such as municipal and county governments) have also played an important role in promoting the popularization and infrastructure building of electric vehicles. Here are some policies and measures taken by local governments in Australia in the field of electric vehicles.
1. City of Sydney
Public charging facilities : The City of Sydney has installed electric vehicle charging stations in multiple car parks and public places in the city and plans to further expand the charging network.
Electric buses : To promote the electrification of public transportation, the City of Sydney has actively introduced electric buses to reduce carbon emissions.
Electric vehicle parking discount : Provide parking fee reduction or discount for electric vehicles in some municipal parking lots.
2. City of Melbourne
Electric Vehicle Promotion : Encourage local residents and businesses to purchase electric vehicles, and explore the possibility of providing parking discounts for electric vehicle owners.
Green building policy : Encourage new commercial and residential projects to reserve electric vehicle charging facilities to support the popularization of electric vehicles in the future.
3. City of Brisbane
Electric vehicle charging stations : The Brisbane City Council has installed electric vehicle charging facilities in several public car parks and along major transportation routes in the city, and plans to continue to expand the charging network in the coming years.
Electric Bus Plan : The City of Brisbane is pushing for the electrification of its bus system to reduce carbon emissions from public transport.
4. City of Adelaide
Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Support : The Adelaide City Council provides multiple public charging stations in the city and plans to continue to increase the number of charging facilities in the future.
Carbon neutrality target : The City of Adelaide is committed to achieving its Carbon neutrality target by actively promoting electric vehicles as part of reducing the city's carbon emissions.
5. City of Perth
Electric vehicle charging facilities : Perth City Council has installed electric vehicle charging stations in several key locations in the city center and plans to further expand the network.
Electric buses : Like other major cities, the City of Perth is pushing for the electrification of its public transport system, including the introduction of electric buses.
6. City of Hobart
Electric Vehicle Promotion : The Hobart City Council is promoting the use of electric vehicles by providing public charging stations and electric vehicle parking discounts in the city.
Sustainable Transport Plan : The City of Hobart is actively pursuing a sustainable transport plan to include electric vehicles as part of the future of urban transport.
7. City of Canberra
Electric Vehicle Incentives : The City Council of Canberra offers electric vehicle parking concessions and has installed multiple charging stations in the city to support the popularity of electric vehicles.
Zero emissions target : The City of Canberra supports the ACT Government's target to make all new car sales zero emission vehicles by 2030.
8. City of Darwin
Infrastructure building : Darwin City Council is gradually installing electric vehicle charging stations in major urban and suburban locations to support the growth of local electric vehicles.
Electrification of public transport : The City of Darwin is exploring the possibility of introducing electric buses and other electric public transport.
Local governments in Australia are mainly promoting the popularization of electric vehicles by expanding charging infrastructure, providing parking discounts, promoting the electrification of public transportation, and working with businesses and communities to achieve these goals. These measures by local governments supplement state and federal policies, making the promotion and application of electric vehicles in Australia more extensive and in-depth.
Partial subsidy examples are as follows:

Source:NSW Building Ready Grant | Charge Hub
Source:Electric Vehicle Charger (Residential and Business) Grants Scheme
The electric vehicle and charging market in Australia is still in its infancy. With the advancement of technology, cost reduction, consumer awakening, and policy changes, it is expected that the sales of electric vehicles and charging station construction in Australia will grow rapidly in the next few years, forming a good development momentum.
Electric vehicle sales will continue to grow, and market share will increase year by year.
According to the data from Electric Vehicle Council, in the first half of 2023, the sales volume of electric vehicles in Australia reached 8,688 units, a year-on-year increase of 120%, accounting for 1.7% of the total new car sales. This trend is encouraging and shows that the demand and acceptance of electric vehicles by Australian consumers are constantly increasing. According to Bloomberg New Energy Finance's forecast, by 2030, the sales volume of electric vehicles in Australia will reach 500,000 units, accounting for 30% of the total new car sales; by 2040, the sales volume of electric vehicles in Australia will reach 1.50 million units, accounting for 70% of the total new car sales.
Electric vehicle brands will become more diversified, and Chinese brands will have greater market space.
So far, the electric vehicle (EV) market in Australia is mainly dominated by the following brands:
Tesla (Tesla) : Tesla has a large market share in the electric vehicle market in Australia, and its Model 3 and Model Y are particularly popular.
BYD (BYD) : As a Chinese electric vehicle manufacturer, BYD's market share in Australia is also gradually increasing, especially its more affordable models.
BMW (BMW) : BMW's i-series electric models, such as the i3 and iX3, have also gained some market share in Australia.
Nissan (Nissan) : Nissan's Leaf model is one of the earlier electric vehicles on the Australian market and still has a share of the market.
Hyundai (Hyundai) : Hyundai's Kona Electric and Ioniq range models also have a presence in the Australia market.
Kia (Kia) : Kia's electric models such as EV6 are also gradually gaining attention in the Australian market.
Other brands : Other brands such as Mercedes-Benz, Audi, Ford, etc. are also gradually introducing electric vehicles, and although the market share is relatively small at present, it is expected to grow over time.
With the continuous opening up of the Australian market, more electric vehicle brands will enter the Australian market, providing consumers with more choices and competition. Chinese brands will have greater market space, especially in the mid-to-low-end market, by providing products with high cost performance, long range, and fast charging to meet the needs and preferences of Australian consumers.
The construction of charging station infrastructure will be accelerated, and the charging network will be more perfect.
Currently, Australia's charging station infrastructure is relatively underdeveloped, with about 4,943 public charging sites and 2,392 charging stations nationwide. This is far from enough compared to Australia's vast land area and strong travel demand. However, with the growth of electric vehicle sales, the demand for charging stations will also increase, prompting the government and enterprises to increase investment and construction in charging infrastructure. The Australian government has supported the construction of more charging stations nationwide through projects such as the Future Fuel Fund to meet the charging needs of electric vehicle users. At the same time, some charging companies are also actively expanding their charging networks, such as Chargefox, Evie Networks, Tritium, etc., to provide more convenient and efficient charging services for electric vehicle users.
The charging market in Australia is a constantly changing and innovative market, influenced and driven by various factors such as the development of electric vehicles, charging technology, policies, consumers, and competitors. Currently, the charging market in Australia is mainly dominated by local companies such as Chargefox, Evie Networks, Tritium, etc. These companies have cooperated with governments, car manufacturers, energy companies, etc. to build and operate charging networks covering the whole country, providing convenient and efficient charging services for electric vehicle users. According to PlugShare's data, Chargefox is the largest charging pile brand in Australia, with over 1,000 charging piles, including over 100 ultra-fast charging piles, covering major cities and highways in Australia. Evie Networks is the second largest charging pile brand in Australia, with over 500 charging piles, including over 80 ultra-fast charging piles, covering the east and south coasts of Australia. Tritium is Australia's largest charging station manufacturer, exporting its products to more than 30 countries worldwide, with approximately 300 charging stations in Australia, including over 50 ultra-fast charging stations.
Australia's largest electric vehicle charging network is operated by Anari Energy . Anari Energy is the largest public electric vehicle charging network in Australia and the entire southern hemisphere, providing a wide range of charging services.
National coverage : The Chargefox network covers major cities and interstate highways in Australia, including from Queensland to Victoria, from NSW to South Australia, and aims to provide charging convenience for electric vehicle owners who travel long distances.
High-speed charging stations : Chargefox offers ultra-fast charging stations up to 350kW, which can provide electric vehicles with a range of about 400 kilometers in 15 minutes. High-power charging stations make long-distance travel more convenient.
Partnerships : Chargefox works with major automakers, state governments and private investors to continuously expand its charging network and provide premium charging services. Partners include BMW, Porsche, Nissan, Jaguar, Hyundai and Kia.
Sustainable energy : Some of Chargefox's charging stations use 100% Renewable Energy to generate electricity, providing users with a more environmentally friendly charging option.
Convenient payment system : Chargefox provides a user-friendly mobile app that allows users to find charging stations, start charging, pay fees and monitor the charging process.
In addition to Chargefox, Australia has several other important electric vehicle charging networks:
Evie Networks : Evie Networks is another important charging network that focuses on fast charging and plans to expand its charging stations nationwide.
Tesla Supercharger Network : Designed specifically for Tesla vehicles, it covers several major cities and transport routes in Australia.
With the support of these networks, electric vehicle owners in Australia can enjoy more convenient and extensive charging services, supporting the popularity and long-distance travel needs of electric vehicles.
According to PlugShare's data, as of July 2023, there are about 4,943 public charging sites and 2,392 charging stations in Australia, including 1,298 conventional charging stations, 365 fast charging stations, and 99 ultra-fast charging stations. From these data, it can be seen that the charging market in Australia is still in the early stages of development, and there is still a lot of room for improvement in the number and coverage of charging piles. As of 2023, Australia's electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure has significantly expanded, and the diversity of charging piles and market brands has further increased. The following is an overview of Australia's electric vehicle charging brands and their market share.
Major charging brands and market share
Market share : Chargefox is Australia's largest electric vehicle charging network operator, operating over 1,000 charging points across the country.
Technical features : Provides ultra-high-speed charging stations up to 350kW and uses partially Renewable Energy.
Coverage : Chargefox has charging stations in major cities and interstate highways across Australia.
Market share : Tesla's SuperCharge network primarily serves Tesla vehicles, but its network coverage is also very extensive, especially in major cities and interstate highways.
Technical features : Provide up to 250kW charging power, which can quickly charge Tesla electric vehicles.
Coverage : Mainly distributed in major areas such as UNSW Wales, Victoria, Queensland and Western Australia.
Market Share : Evie Networks is one of the fastest growing electric vehicle charging networks in Australia, committed to providing electric vehicle owners with fast and convenient charging services.
Technical features : Mainly provide 50kW to 350kW fast charging stations, supporting various types of electric vehicles.
Coverage : The network has sites in major cities and transport hubs, with plans for further expansion.
Market Share : JET Charge is a brand that mainly provides residential and commercial charging solutions, but its number of public charging stations is also gradually increasing.
Technical features : Provide charging equipment from 7kW to 50kW, supporting multi-brand electric vehicles.
Coverage : Charging services are mainly provided in urban centers and corporate parks.
Market share : UNSW Welsh road services company NRMA operates an electric vehicle charging network mainly concentrated in UNSW Wales.
Technical features : Provide fast charging stations from 50kW to 350kW.
Coverage : NRMA operates multiple charging stations across major cities and tourist routes in UNSW Wales.
In addition to the main brands mentioned above, there are many other brands in the Australian charging market, such as ABB, Delta, EO, EVNex, FIMER, Fronius, GoodWE, Hypervolt, KEBA, Ocular, Schneider, SMA, Smappee, Solar Edge, Wallbox, Zappi, etc. The following is a basic introduction to each charging brand.
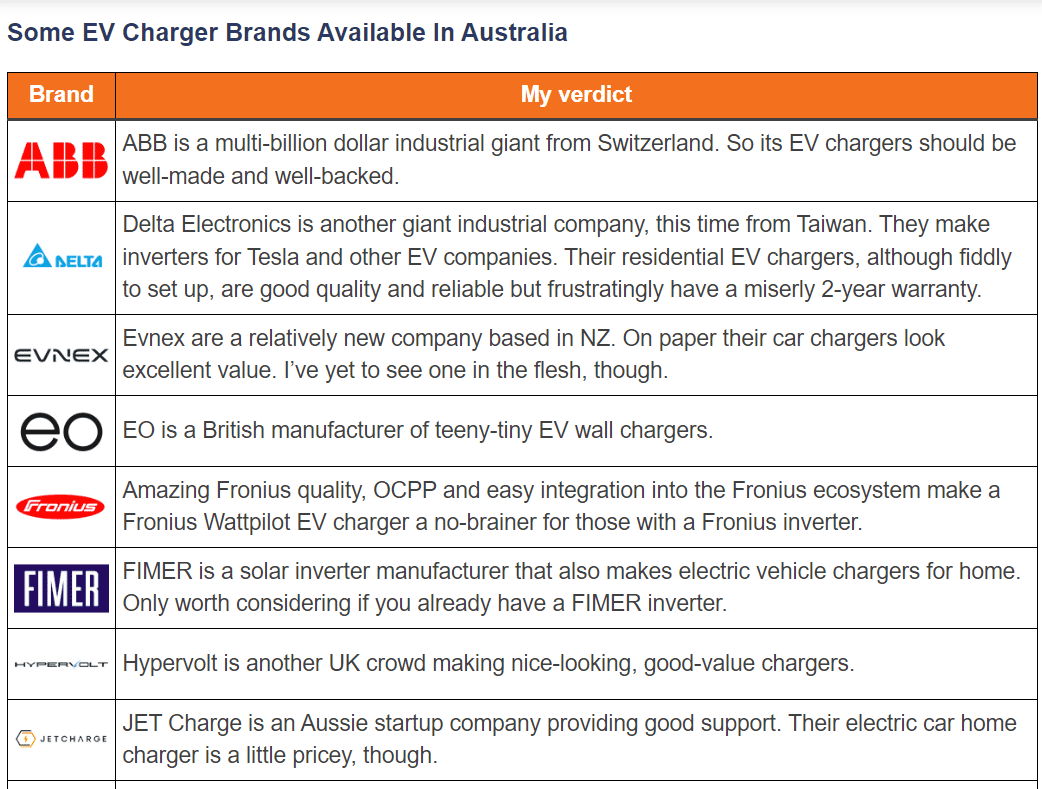

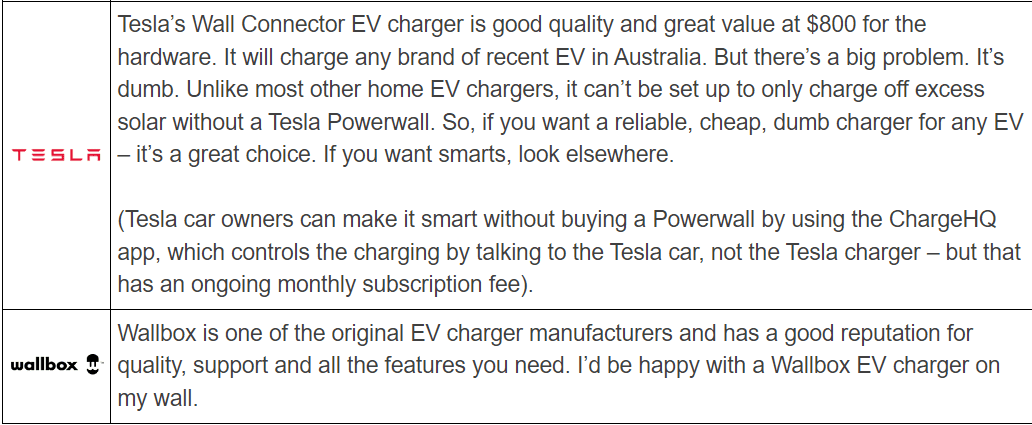
Source:www.solarquotes.com.au
Due to the rapid growth of the electric vehicle charging market in Australia, the exact market share data may change at any time. Generally, Chargefox and Tesla Supercharger are the two operators with the largest market share, while emerging brands such as Evie Networks and JET Charge are also rapidly expanding. With the increasing popularity of electric vehicles, it is expected that the number of charging station and brand competition will further increase. Continued investment from the government and private investors will prompt more charging facility construction, especially in remote areas and along interstate highways, to support long-distance travel and wider use of electric vehicles.
In conclusion, high-speed DC charging systems play a pivotal role in accelerating the growth and success of electric vehicles (EVs) worldwide. These systems not only enhance convenience for EV users but also contribute significantly to the advancement of sustainable transportation. For individuals or businesses looking to invest in top-quality DC fast chargers, Anari stands out as a reliable and trusted choice.
As a leading DC fast charger manufacturer and supplier based in China, Anari has earned a reputation for excellence through its commitment to quality, innovation, and customer satisfaction. The company’s products adhere to international standards, ensuring reliability and compatibility with diverse EV models. Whether you are an EV owner, fleet operator, or infrastructure developer, Anari’s comprehensive range of DC fast chargers is designed to meet your specific needs.
Read more:
Top 10 EV Charger Manufacturers in the USA in 2025
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Install an Electric Car Charging Station
Top 10 EV Charging Companies in the World 2025
The state of EV Charging in the Middle East Region - Anari Energy







